API 13A is short for ANSI/API Specification 13A. This international standard covers materials that are in common usage in petroleum and natural-gas drilling fluids. The intent of the document is to incorporate all international standards for drilling fluid materials into an ISO formatted document. It covers physical properties and test procedures for materials manufactured for use in oil- and gas-well drilling fluids. CMC, as one of the key additives in this industry, is also listed in the document, specifically low-viscosity carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-LVT) and high-viscosity carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-HVT).
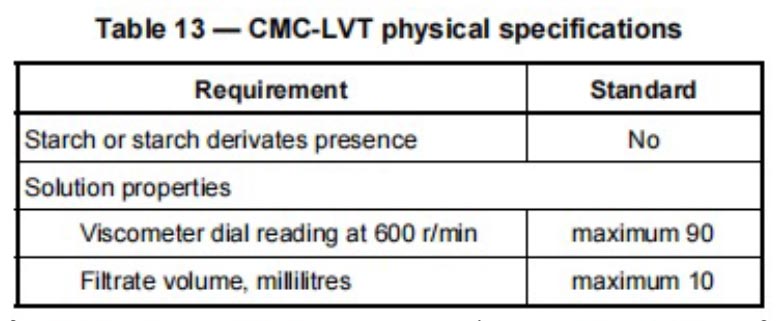
Technical-grade low-viscosity CMC (CMC-LVT)
Technical-grade high-viscosity CMC (CMC-HVT)
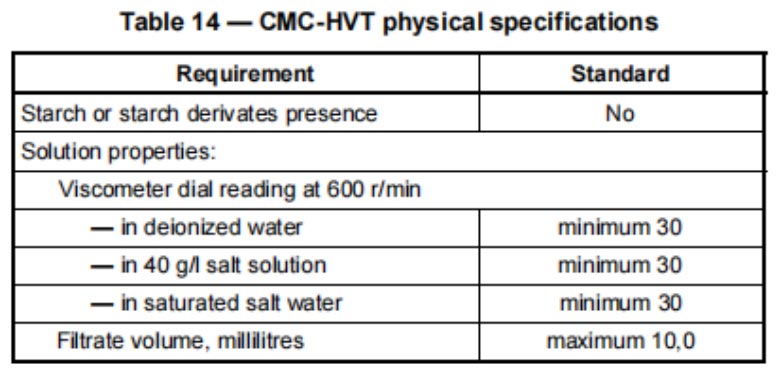
Technical-grade CMC (CMC-LVT and CMC-HVT) is an alkali metal salt of carboxymethyl cellulose. It is a free-flowing or granulated powder and is not normally purified of by-products formed in the reaction. API 13A clearly states that CMC should be free from any starch or starch derivatives. It specifies clear and strict requirements for the viscosity of CMC. However, this viscosity is not measured in the conventional unit of mPa.s, but defined by the dial reading of a standard rotational viscometer at a rotational speed of 600 r/min. Specifically, the viscometer dial reading of CMC-LVT should be no more than 90, while the viscometer dial readings of CMC-HVT in deionized water, 40g/l salt water, and saturated salt water shall all be no less than 30. This indicator ensures that in different drilling fluid systems such as fresh water and salt water, it can effectively increase the system viscosity and meet the operational requirements of carrying cuttings and protecting the wellbore. The maximum filtrate volume shall generally not exceed 10 ml, so as to reduce the leakage of drilling fluid into the formation and prevent wellbore collapse.
If you are interested in API 13A oil-drilling grade CMC, please feel free to contact us.
SINOCMC Team
